Prototype Model
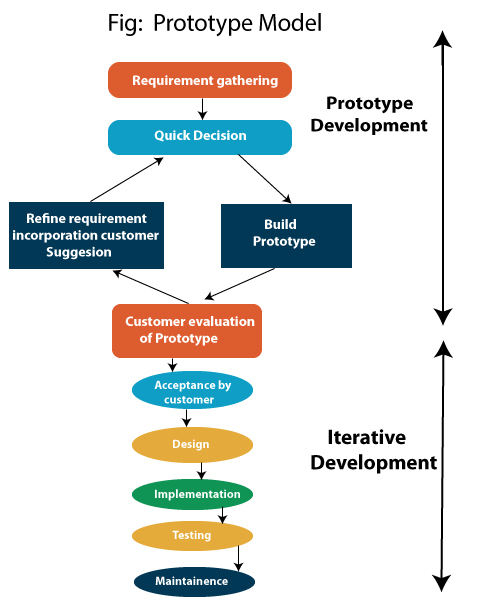
Prototype Model. Software prototyping, a possible activity during software development, is the creation of prototypes, i.e., incomplete versions of the software. A prototype is an original model, form or an instance that serves as a basis for other processes. In software technology, the term prototype is a working example through which a new model or a new version of an existing product can be derived.
The basic idea in Prototype model is that instead of freezing the requirements before a design or coding can proceed, a throwaway prototype is built to understand the requirements. This prototype is developed based on the currently known requirements. Prototype model is a software development model. By using this prototype, the client can get an “actual feel” of the system, since the interactions with prototype can enable the client to better understand the requirements of the desired system. Prototyping is an attractive idea for complicated and large systems for which there is no manual process or existing system to help determining the requirements.
The prototype are usually not complete systems and many of the details are not built in the prototype. The goal is to provide a system with overall functionality.
Diagram of Prototype model:
Advantages of Prototype model:
- Users are actively involved in the development
- Since in this methodology a working model of the system is provided, the users get a better understanding of the system being developed.
- Errors can be detected much earlier.
- Quicker user feedback is available leading to better solutions.
- Missing functionality can be identified easily
- Confusing or difficult functions can be identified
Requirements validation, Quick implementation of, incomplete, but
functional, application.
Disadvantages of Prototype model:
- Leads to implementing and then repairing way of building systems.
- Practically, this methodology may increase the complexity of the system as scope of the system may expand beyond original plans.
- Incomplete application may cause application not to be used as the
full system was designed
Incomplete or inadequate problem analysis.
When to use Prototype model:Â Â
- Prototype model should be used when the desired system needs to have a lot of interaction with the end users.
- Typically, online systems, web interfaces have a very high amount of interaction with end users, are best suited for Prototype model. It might take a while for a system to be built that allows ease of use and needs minimal training for the end user.
- Prototyping ensures that the end users constantly work with the system and provide a feedback which is incorporated in the prototype to result in a useable system. They are excellent for designing good human computer interface systems.
You might also be interested in :
What is Waterfall model?
What is Agile Model?
What is V-model?
What is Incremental model?
What is Spiral model?
What is RAD model?
Other popular articles:
You're reading Entrepreneur India, an international franchise of Entrepreneur Media.
We frequently come across different types of prototypes and their applications but do not clearly understand the real purpose or necessity of the application of the prototype. We get questions like how good should the prototype be? Does it need to work properly? A prototype is a basic working model, mock-up or a simple simulation of the product which leads us to create a minimal viable product to final product and variations. The main reason for prototyping is to validate the idea and this is the step in converting an idea to a real product. A prototype could be a working model, representational (non-working) model, miniature or a scale model, video or a photo demonstration based on the factors like a problem to be solved, the mandate of the end customer, investor/industry requirements or prototype that best satisfies the purpose. Ideally, the first type should be a working model which is actually functional, so people can get their hands on it and try it out. Also, it good to get the wrinkles ironed out before presenting the prototype to industry —as not very often a second meeting is given in case prototype fizzles at a meeting. But sometimes it isn’t possible to have a working model, in such cases another kind of prototypes is used which best suits the situation.
A prototype can be in the following forms paper, 3D printing, digital, small model or limited usage product. These prototypes can fall into one of the following area functional, display or a small model. The functional prototype focus on the functions and not on the looks. The display prototype focuses on the looks and not so much on the function. The small model combines both and is a smaller version of the final product. They type of prototype to develop must be decided based on the intended purpose of the prototype, the medium of use and the expected longevity of the prototype.
Prototypes can be throwable or non-throwable types. Both have their own benefits a throwable type is done just to get an idea of a product, a non-throwable is one which improvements can be made to arrive at the final product.
There are many types of the prototype here is ten of those types: -
- A film (movie) prototype
Here a prototype is made using video just to show others the idea in a graphical/visual format.
2. Feasibility Prototype
This type of prototype is usually developed to determine the feasibility of various solutions. It is applied to the resolve technical risks attached to the development in terms of performance, compatibility of components etc.
3. Horizontal Prototype
This is the user interface in the form of screenshots, demonstrating the outer layer of the human interface only, such as windows, menus, and screens. The prototype is used to clarify the scope and requirements of the product.
4. Rapid Prototype
The rapid prototyping technique is used to quickly engineer an initial model of a product using a three-dimensional computer-aided design when you want to produce something in a short span.

5. Simulations
Simulation prototype is digitally creating of a physical product to predict the performance of the product in the real world. Geist elementary kindergarten registration.
6. Storyboard
A storyboard describes a product in a form of a story and demonstrates a typical order in which information needs to be presented. It helps in determining useable sequences for presenting information
7. Vertical Prototype
A vertical prototype is the back end of a product like a database generation to test front end. It used to improve database design, test key components at early stages or showcase a working model, though unfinished, to check the key functions.
8. Wireframe
This is a skeleton a product. Depicted in the form of illustrations or schematics that capture an aspect of design such as an idea, layout, form, architecture or sequence.
9. Animations
These are images drawn and put in a sequence that walks you through the proposed 3D structure of the product/solution.
10. Mock-up
This is with no functionalities, just to get overall visual of the product. It is an unpolished version of the product with no active features.
In conclusion, depending on what you are working on you will need to decide which prototype works best for you, often a number of these might need to be used into a working prototype.